Many people believe that vegan diets fail to provide satiety since it may be difficult to feel satisfied and full without animal products. However, making nutritious and fulfilling meals that stick to your nutritional demands is possible if you thoroughly understand plant-based nutrition. This article will look into how to feel full on a vegan diet.
Understanding Proper Plant-Based Nutrition for Satiety
Concentrating on the key components of a satisfying meal is important if you want to feel full on a vegan diet. These include consuming enough fiber and staying hydrated and macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats).
Key Components of a Filling Vegan Meal
Macro Nutrients
Macronutrients are essential for satiety. Energy-giving carbohydrates are present in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables. You can increase feelings of fullness by including complex carbs like quinoa, brown rice, and sweet potatoes in your meals.
Proteins
Proteins are essential for maintaining and repairing muscles. Tofu, tempeh, lentils, beans, chickpeas, and quinoa are all vegan protein sources. These protein-rich foods can increase satiety when incorporated into your meals.
Fats
Feeling satisfied and full can be affected by fats as well. Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are good plant-based fat sources. Your meals can be enhanced by including a small amount of healthy fats while providing the necessary nutrients.
Fiber
Consuming enough fiber is essential to healthy digestion and feeling full. Legumes, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and nuts are a few foods high in fiber. These foods offer meals more weight and take longer to digest, which increases satiety.
Incorporating High-Fiber Foods into Your Diet
Foods high in fiber have various benefits for satiety. They support a sense of fullness, slow digestion, and gradually give off energy. They also promote intestinal health and might help with weight management.
Here is a list of high-fiber vegan foods:

Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and kidney beans are excellent sources of fiber and protein.
Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat products provide fiber and complex carbohydrates.
Fruits: The high fiber content of berries, apples, pears, and bananas makes them excellent snacks or addition to meals.
Vegetables: Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, spinach, and kale are rich in fiber and other essential nutrients.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts offer healthy fats and fiber.
To Incorporate High-fiber Foods into Your Diet, Consider The Following
- Kick-start your day with a fiber-rich breakfast like overnight oats topped with berries and seeds.
- Incorporate legumes into soups, stews, or salads.
- Prefer whole grains instead of refined grains for meals like quinoa stir-fry or brown rice bowls.
- Consider fresh fruits and raw vegetables as snacks.
- Include nuts and seeds in your meals, or enjoy them as a snack.
Plant-Based Protein Sources for Satiety
Protein is an essential component for feeling full on a vegan diet. It contributes to satiety by regulating hunger hormones. Luckily, there are many plant-based protein sources available.
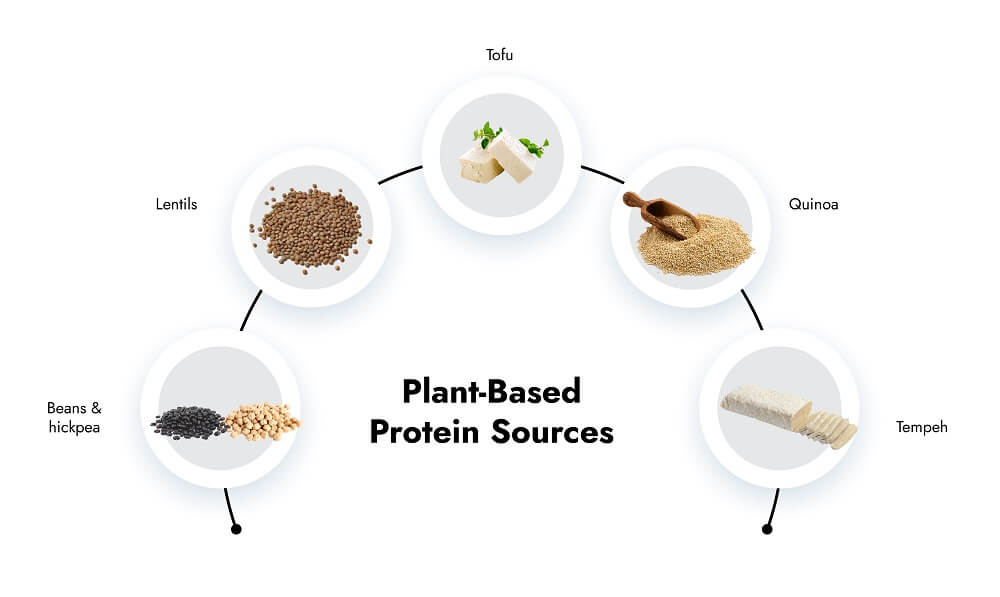
Here are some protein-rich plant-based foods
1. Tempeh and Tofu: Tempeh and Tofu are made from soybeans and are excellent protein sources. They can be used in stir-fries, sandwiches, or grilled as a main course.
2. Lentils: Lentils are affordable and protein-packed legumes. They can be used in stews, soups, or salads.
3. Quinoa: Quinoa is a pure protein source and can be used as a main ingredient for salads, pilafs, or stuffed vegetables.
4. Beans and Chickpeas: Black beans, kidney beans, and chickpeas have a high amount of protein and can be used in various dishes like chili, curries, or hummus.
To increase your protein intake, consider the following
• Adding tofu or tempeh to stir-fries, wraps, or sandwiches.
• Using lentils as an alternative to meat in dishes like spaghetti bolognese or tacos.
• Experimenting with quinoa salads or using it as a side dish.
• Including beans or chickpeas in soups, stews, or casseroles.
Healthy Fats on a Vegan Diet
Healthy fats are essential for satiety and overall health. They deliver satisfaction, contribute to nutrient absorption, and support brain function. Vegan sources of healthy fats include:

• Avocados: Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats and can be added to salads, mashed onto toast, or blended into smoothies.
• Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, cashews, and pistachios are loaded with healthy fats and can be enjoyed as a snack or added to meals.
• Seeds: Chia seeds, flaxseeds, and hemp seeds are high in omega-3 fatty acids and can be topped onto yogurt or oatmeal or used in baking.
• Nut Butter: Peanut butter, almond butter, or cashew butter can be spread on whole-grain or multi-grain bread, added to smoothies, or used as a dip for fruits and vegetables.
To include healthy fats in your meals and snacks, try the following
• Adding sliced avocado to salads, wraps, or sandwiches.
• Including a handful of nuts as a snack or topping for salads and stir-fries.
• Sprinkling seeds as a topping on your morning cereal, yogurt, or salads.
• Use nut butter to spread or dip for fruits, whole-grain crackers, or celery sticks.
Meal Planning for Satiety on a Vegan Diet
Effective meal planning on a vegan diet can help you meet your satiety and nutritional needs.
Here are some tips to remember:
Balance and Variety: Include a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) in every meal. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and plant-based proteins to ensure you get a wide range of nutrients.
Portion Control: Focus more on portion sizes to avoid overeating. Use measuring cups, kitchen scales, or visual cues to know portion sizes and avoid consuming too many calories.
Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating by enjoying each bite, eating slowly, and paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness signals. This can help prevent overeating and promote a greater sense of satisfaction.
Preparing in Advance: Plan your meals, batch cook when possible, and have healthy snacks. Avoid choosing unhealthy and less nutrient foods when you are hungry.
Seek Recipe Inspiration: Explore vegan cookbooks, websites, or social media platforms for recipe ideas that prioritize satiety and nutrition. Experiment with new ingredients and flavors to keep your meals tasty and satisfying.
Conclusion
By incorporating these tips into your meal planning routine, you can create balanced and satisfying vegan meals that promote satiety and support your overall health. Remember to consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personal advice based on your specific dietary needs and goals.
