It’s important to remember that vitamins work best alongside a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the essential nutrients your skin needs to thrive. Adequate sleep, hydration, and proper skin care practices are significant in achieving clear skin. It’s important to note that while these vitamins can contribute to clear skin, they are not a cure-all. Factors like diet, stress levels, and genetics can also affect skin health.
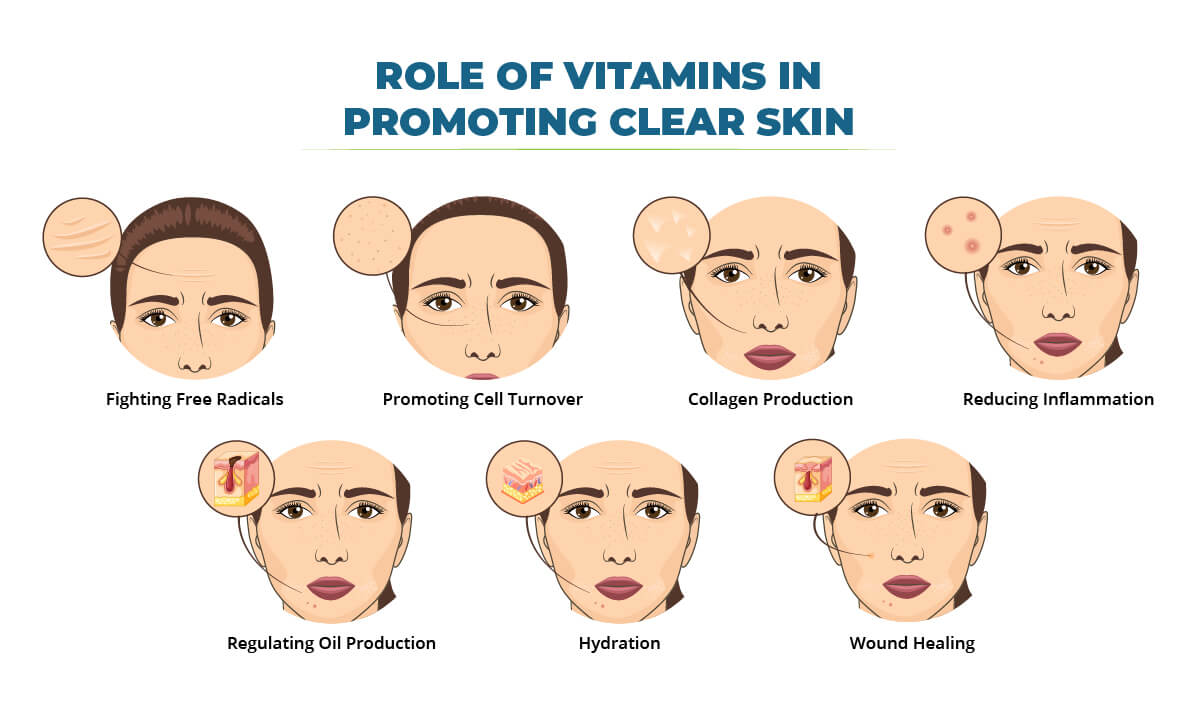
Role of Vitamins in Promoting Clear Skin
Fighting Free Radicals: Antioxidant vitamins like A, C, and E neutralize harmful free radicals, unstable molecules formed by the body’s natural processes, and environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals damage skin cells and contribute to wrinkles and premature aging. These vitamins help keep skin healthy and resilient by mopping up these free radicals.
Promoting Cell Turnover: Vitamin A is crucial in regulating skin cell turnover. Skin cells are naturally replaced by new ones, but with age, this process slows down, causing a buildup of dead skin cells on the surface. This can clog pores and contribute to breakouts. Vitamin A helps shed dead skin cells, keeping pores clear and promoting smoother, clearer skin.
Collagen Production: Vitamin C is necessary for the production of collagen, which provides structure and elasticity to the skin. Adequate collagen keeps skin firm and youthful, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. As we age, collagen production naturally decreases. Vitamin C helps stimulate collagen production, keeping skin plump and supple.
Reducing Inflammation: Vitamin E has anti-inflammatory properties that help soothe and calm irritated skin. This can be useful for conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Inflammation can cause redness, swelling, and discomfort. Vitamin E’s anti-inflammatory effects can help reduce these symptoms and promote healing. It may also aid in reducing acne scarring by minimizing inflammation that can contribute to scar formation.
Regulating Oil Production: Zinc helps regulate the production of sebum, the skin’s natural oil. Excessive sebum production can lead to acne by clogging pores. Zinc’s antibacterial properties and ability to regulate oil production promote clearer skin.
Hydration: The Vitamin B complex, particularly B3 (niacinamide) and B5 (pantothenic acid), helps the skin retain moisture. Dehydrated skin can appear dull and rough and worsen the wrinkles and fine lines. B vitamins contribute to a plump and dewy complexion by keeping the skin hydrated.
Wound Healing: Vitamin C and zinc play a role in wound healing. They can help accelerate the healing of blemishes and minor skin irritations, promoting a smoother, more even skin tone.
Many strive for clear, healthy skin. Beyond aesthetics, clear skin reflects overall well-being. While genetics and external factors can influence skin health, what we put into our bodies plays a crucial role. This article delves into vitamins, exploring how specific ones can contribute to a radiant complexion.
Antioxidant Allies: Vitamins A, C, E, and Zinc
Our skin is continuously exposed to environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution. These elements generate free radicals, unstable molecules that damage skin cells and accelerate aging. This is where antioxidant vitamins come in as powerful allies.
Vitamins That Can Contribute to Clear Skin
Vitamin A
Often referred to as the “retinol vitamin,” vitamin A plays a multifaceted role in skin health. It boasts potent antioxidant properties, neutralizing free radicals contributing to premature aging and wrinkles. By scavenging these free radicals, vitamin A helps protect the skin’s structural components, such as collagen and elastin, from damage. Collagen provides the skin with its plumpness and structure. At the same time, elastin allows it to maintain its elasticity and bounce back from stretching. When free radicals damage these components, the skin loses its firmness, and wrinkles become more noticeable.
Vitamin A not only acts as an antioxidant but also plays an important role in regulating the turnover of skin cells. As we age, this process slows down, accumulating dead skin cells on the surface. This, in turn, can block pores and create an environment conducive to breakouts. However, vitamin A helps maintain a healthy rate of skin cell shedding, thereby preventing clogged pores and promoting a smoother and clearer complexion. Additionally, vitamin A can stimulate the production of new skin cells, thus improving the overall appearance and texture of the skin.
Vitamin A is multifaceted in promoting clear skin by addressing several factors contributing to blemishes and breakouts. Here’s a closer look at how this essential nutrient benefits your complexion:
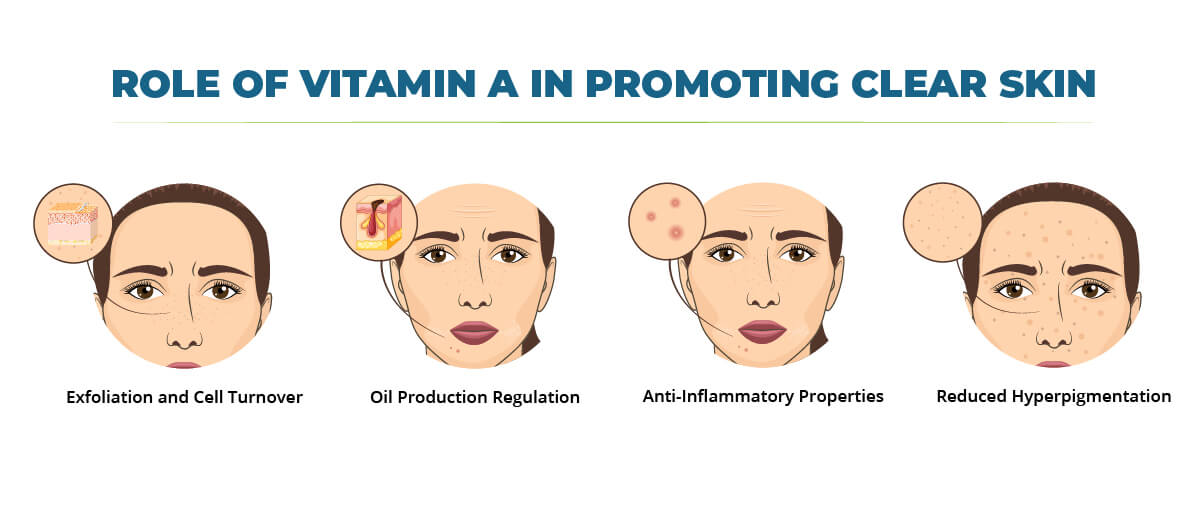
Exfoliation and Cell Turnover: Vitamin A is a normalizing agent for skin cell turnover. Skin cells naturally shed throughout the day, allowing new ones to be replaced. This process is essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin. However, when dead skin cells don’t shed effectively, they can build up on the surface and clog pores. This clogged pore environment is a prime breeding ground for acne-causing bacteria, leading to breakouts. Vitamin A, particularly retinol, helps regulate the shedding of old skin cells and promotes the production of new ones. This gentle exfoliation destakes clogged pores, preventing future breakouts and contributing to a smoother, clearer complexion. Additionally, regular exfoliation can help minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles by improving production of collagen. This protein provides skin structure and elasticity.
Oil Production Regulation: Vitamin A can help regulate sebum production, the oil naturally secreted by the skin. Sebum plays a vital role in keeping skin hydrated and supple. However, excessive sebum production can be problematic, especially for oily skin patients. When the natural oil produced by the skin mixes with dead skin cells and dirt, pores can clog and lead to acne breakouts. Retinoids, which are powerful derivatives of vitamin A, are known to regulate the production of sebum. By binding to receptors in skin cells and influencing the genes that control sebum production, vitamin A helps prevent the formation of clogged pores and breakouts, thus promoting clearer skin.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Acne is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. These blemishes develop when sebum and dead skin cells become trapped within pores, creating a breeding ground for bacteria. The body’s immune system responds to this bacterial invasion by sending white blood cells to fight the infection. This inflammatory response causes redness, swelling, and pus associated with acne lesions. Vitamin A, particularly retinoids, possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe and reduce redness associated with acne lesions. By mitigating inflammation, vitamin A can minimize the severity of breakouts, promote faster healing, and reduce the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots left behind by acne).
Reduced Hyperpigmentation: Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition that causes certain areas of the skin to darken. Various factors, such as sun damage, acne breakouts, and hormonal changes, can cause it. The pigment melanin plays a crucial role in hyperpigmentation. When melanin production is stimulated by the sun or other factors, it can result in dark spots or patches on the skin. Vitamin A, specifically certain retinoids, can help regulate melanin production by slowing down the activity of tyrosinase. This could reduce hyperpigmentation and promote a more even skin tone. Retinoids can be helpful for individuals struggling with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots left behind by acne) or other forms of hyperpigmentation, such as sun damage or melasma.
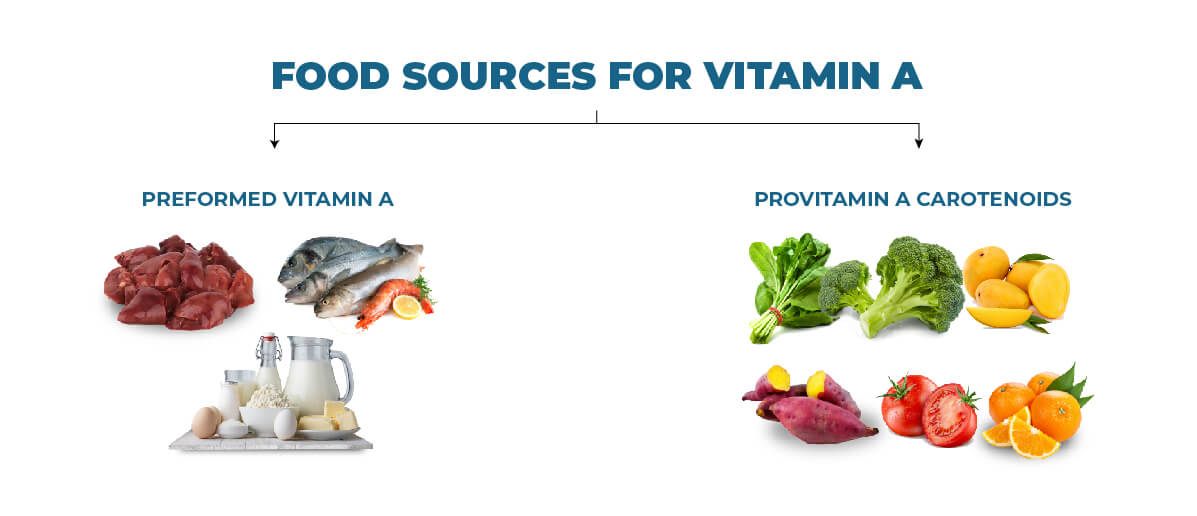
Food Sources For vitamin A
Vitamin A comes in two main forms:
- Preformed Vitamin A (Retinol): This form is found directly in animal-based foods and is readily absorbed by the body. It’s the most efficient way for humans to get vitamin A, as it doesn’t require any conversion within the body.
- Provitamin A Carotenoids: The body must convert these plant-based pigments, also known as precursors, into retinol (vitamin A). The conversion process takes place in the small intestine. It can be affected by several factors, such as overall dietary fat intake and individual variations in metabolism.
Here’s a breakdown of food sources for both types of vitamin A:
Preformed Vitamin A (Retinol)
Animal Products:
- Liver: Beef liver is exceptionally rich in preformed vitamin A, but consume it moderately due to high vitamin A content.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, cod, herring, and tuna (especially fish liver oils) are excellent sources.
- Whole Milk and Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt, particularly whole-fat options, contribute to preformed vitamin A.
Eggs: A good source of both preformed vitamin A and carotenoids.
Provitamin A Carotenoids
Orange and Yellow Fruits and Vegetables: These are classic sources of carotenoids, especially beta-carotene. Examples include:
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Cantaloupe
- Mangoes
- Apricots
Dark Leafy Greens: They offer carotenoids like lutein and beta-carotene. Examples include:
- Kale
- Spinach
- Collard greens
- Swiss chard
Other Fruits and Vegetables
- Tomatoes (especially cooked tomatoes)
- Red bell peppers
- Broccoli
Additional Considerations
- Fat-Soluble: Both preformed vitamin A and carotenoids are fat-soluble. Including healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, or nuts in your meals can aid in their absorption.
- Conversion Rate: The efficiency of converting carotenoids to retinol can vary depending on individual factors.
- Variety is Key: Add a diverse range of foods from both categories to ensure a good mix of preformed vitamin A and provitamin A carotenoids.
Tips for Maximizing Vitamin A Absorption
- Consume vitamin A-rich plant foods with healthy fats, like nuts, seeds, or avocado oil. Fat aids in the absorption of carotenoids from plant sources.
- Cook some vegetables, particularly carrots, with oil to enhance carotenoid absorption.
- Store fruits and vegetables properly to minimize nutrient loss.
Vitamin C
Another key antioxidant, vitamin C, protects the skin from sun damage. It’s essential for collagen production, the protein that gives skin its structure and youthful plumpness. As collagen production declines with age, wrinkles and fine lines become more prominent. By promoting collagen synthesis, vitamin C helps maintain skin’s elasticity and reduce the wrinkles.
Vitamin C is a multifaceted nutrient that plays a vital role in promoting clear, healthy skin. Here’s a breakdown of its key benefits:
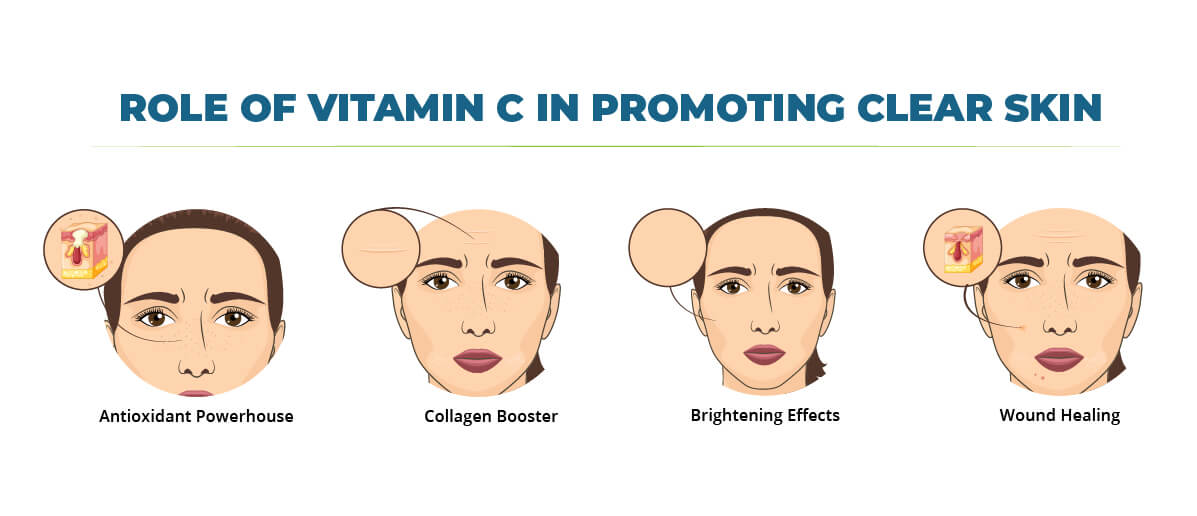
- Antioxidant Powerhouse: Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that protects the skin from harmful free radicals, unstable molecules produced by natural processes and environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution. These free radicals damage skin cells, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation (dark spots). By neutralizing free radicals, vitamin C helps protect the skin from these damaging effects, promoting a more youthful and even-toned complexion. In addition, vitamin C acts as the skin’s first line of defense against environmental aggressors and prevents the visible signs of aging and sun damage.
- Collagen Booster: Collagen is a highly available protein in the skin that provides structure, firmness, and elasticity. However, collagen production naturally declines with age. Vitamin C is a cofactor in collagen synthesis, meaning it’s essential for producing this vital protein. By stimulating collagen production, vitamin C helps maintain the skin’s youthful plumpness and reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Think of vitamin C as the scaffolding that provides the underlying support for a firm, youthful complexion.
- Brightening Effects: Vitamin C can help reduce hyperpigmentation, which is the darkening of certain areas of skin. It does this by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Vitamin C has the potential to reduce the production of melanin and even out skin tone, thus helping to lighten dark spots. It can be helpful for individuals who are dealing with sun damage, acne scars, or other forms of hyperpigmentation. By regulating the production of melanin, Vitamin C can help you achieve a bright and radiant complexion.
- Wound Healing: Vitamin C plays a major role in wound healing by aiding in the production of collagen and promoting tissue repair. This can benefit acne breakouts, as it helps wounds heal faster and minimize scarring.
Additional Considerations
- Topical vs. Oral Vitamin C: Vitamin C can be applied topically through serums or creams. However, research suggests that oral vitamin C intake might be more effective for overall skin health benefits due to its ability to reach deeper layers of the skin. Topical vitamin C can still offer some benefits, but oral intake may be less potent.
- Sun Protection Partner: While vitamin C offers sun protection benefits by neutralizing free radicals, it’s not a substitute for sunscreen. Sun exposure is a major contributor to free radical damage and premature skin aging. Always use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days. Sunscreen protects from UV rays and prevents sunburn, hypertension, and wrinkles.
- Choosing the Right Vitamin C Product: Look for serums with L-ascorbic acid, the most effective form of topical vitamin C. However, L-ascorbic acid can be unstable and break down in sunlight or heat. Choose a product with a stable form of vitamin C, like sodium ascorbyl phosphate or magnesium ascorbyl phosphate, and store it in a cool, dark place to maximize its effectiveness.
Food Sources of Vitamin C
Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons), berries (strawberries, blueberries), kiwifruit, bell peppers, tomatoes.
Vitamin C is water-soluble, meaning the body doesn’t store it for long periods. Unlike fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), vitamin C is readily excreted through urine. Therefore, to maintain optimal levels and reap its numerous health benefits, including promoting clear, healthy skin, incorporating a variety of vitamin C-rich foods in your daily diet is crucial. Consuming these foods regularly ensures a consistent supply of this nutrient for your body.
However, our bodies don’t synthesize vitamin C, so we must rely on dietary sources to meet our daily requirements. The recommended daily intake (RDI) for vitamin C can differ depending on age and gender, but for adults, it’s 75 milligrams (mg) for women and 90 mg for men. Smokers and those with certain health conditions may require even higher intakes.
By including various vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables throughout the week, you can ensure you meet your daily needs and provide your body with the essential nutrients it requires for optimal functioning. Here’s a breakdown of some excellent sources:

Fruits
- Citrus Fruits (Highest in Vitamin C): Oranges, grapefruits, lemons, limes, tangerines, kiwifruit
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, blackberries
- Tropical Fruits: Papaya, pineapple, guava, mango
Vegetables
- Bell Peppers (Highest in Vitamin C among Vegetables): Red, green, yellow, orange
- Broccoli: A cruciferous vegetable rich in vitamin C and other antioxidants.
- Tomatoes: A good source of vitamin C and the antioxidant lycopene, beneficial for skin health.
- Dark Leafy Greens: Kale, spinach, collard greens, Swiss chard
- Brussels Sprouts: Another cruciferous vegetable offering vitamin C and other beneficial nutrients.
Other Sources
- Potatoes: While not the most concentrated source, potatoes can contribute vitamin C, especially when eaten with the skin on.
Tips for Maximizing Vitamin C Intake
- Fresh is Best: Vitamin C can degrade over time. Choose fresh fruits and vegetables whenever possible, as they offer the highest vitamin C content.
- Cooking Methods: While some cooking is necessary for certain vegetables, minimize cooking time to retain vitamin C content. Steaming or lightly boiling are better methods compared to frying or overcooking.
- Eat Soon After Cutting: Fruits and vegetables exposed to air for extended periods can lose vitamin C. Cut them just before consumption to minimize nutrient loss.
- Variety is Key: Include various vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables in your diet to ensure you’re getting a good balance of this essential nutrient.
Additional Considerations
- Vitamin C and Citrus Fruits: While citrus fruits are often associated with vitamin C, other fruits and vegetables offer significant amounts of vitamin C. In addition to citrus, you can also eat other fruits and vegetables to broaden your dietary intake and benefit from a range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Vitamin C Supplements: Consult your doctor before taking vitamin C supplements. While they can be helpful in certain cases, most healthy individuals can meet their vitamin C needs through a balanced diet.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E plays a dual role in promoting clear skin, acting as an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory agent. This vitamin acts as a double agent, providing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits. Vitamin E shields the skin from free radical damage and can soothe irritation. It helps reduce irritation and scarring by minimizing inflammation, which can contribute to scar formation. Here’s a closer look at how it benefits your complexion:
- Antioxidant Shield: Like vitamins A and C, vitamin E is a potent antioxidant. It combats free radicals, unstable molecules produced by the body’s natural processes, and environmental factors like UV radiation and pollution. Free radicals damage skin cells, contributing to wrinkles, premature aging, and hyperpigmentation. Vitamin E is a shield, neutralizing these free radicals and protecting the skin from their harmful effects. This helps maintain a more youthful and even-toned complexion.
- Soothing Inflammation: Acne, eczema, and psoriasis are all skin conditions characterized by inflammation. Vitamin E’s anti-inflammatory properties can help soothe and calm irritated skin. It may also reduce redness and discomfort associated with these conditions. Furthermore, vitamin E can minimize scarring from acne breakouts by reducing inflammation. As inflammation contributes to scar formation, reducing inflammation with vitamin E may help promote healing and minimize the appearance of scars.
- Potential Benefits for Wound Healing: Vitamin E plays a role in wound healing by supporting tissue repair. This can benefit acne breakouts, as it can help wounds heal faster and potentially minimize scarring. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that topical vitamin E may help improve the appearance of acne scars. Studies prove that vitamin E supplementation can shorten the healing time of wounds, including surgical incisions.
- Moisturizing Properties: Vitamin E has mild moisturizing properties, which can benefit those with dry skin. It helps maintain the skin’s natural moisture barrier, preventing dryness and flaking. While not a substitute for a moisturizer, vitamin E can provide additional hydration support, especially for dry or sensitive skin.
- Sun Protection Partner (indirectly): While vitamin E doesn’t directly block UV rays like sunscreen, it can offer some indirect sun protection by neutralizing free radicals generated by UV exposure. This can help minimize some of the damaging effects of the sun on the skin. However, it’s crucial to remember that vitamin E is not a substitute for sunscreen. Always use suncreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days, for optimal sun protection.
Here are some additional points to consider:
Topical vs. Oral Vitamin E: Vitamin E can be applied topically through creams or oils. While topical application may offer some benefits for localized concerns, research suggests that oral consumption of vitamin E might be more effective for overall skin health benefits due to its ability to reach deeper layers of the skin. Consider both options, but consult a dermatologist to determine the best approach for your needs.
Choosing the Right Topical Vitamin E Product: Look for products containing tocopherol, the most active form of vitamin E. However, topical vitamin E can be sensitive to light and heat. Choose a product packaged in an opaque container and store it in a cool, dark place to maximize its effectiveness.
When promoting clear skin and overall health, incorporating a variety of vitamin E-rich foods into your diet is essential. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that offers numerous benefits, including protecting your skin from damage and potentially reducing inflammation. Here’s a breakdown of some excellent food sources to add to your plate:
Top Sources of Vitamin E

- Nuts and Seeds: These powerhouses are at the top of the list for vitamin E content. Some of the richest options include Almonds, sunflower seeds, peanuts, and hazelnuts.
- Avocado: This creamy fruit is delicious and a fantastic source of vitamin E (3.1 mg per half). Avocados have several benefits and can be enjoyed in salads, toast toppings, guacamole, or smoothies.
- Olive Oil: It is a healthy fat rich in vitamin E (1.9 mg per tablespoon). Use it for salad dressings, cooking (at moderate temperatures), or drizzling over vegetables.
Other Good Sources
- Spinach: This leafy green powerhouse offers vitamin E (1.5 mg per cup) and a wealth of other vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, tuna, and other fatty fish are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids and also provide a good amount of vitamin E (1.0 mg per 3 oz cooked serving).
Tips for Maximizing Vitamin E Absorption
- Pair with Healthy Fats: Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, meaning it is better absorbed when consumed with healthy fats. Enjoy your vitamin E-rich foods alongside nuts, seeds, avocado, or a drizzle of olive oil.
- Cooking Methods: While some cooking is necessary for certain vegetables, minimize cooking time and harsh methods like frying to preserve vitamin E content. Steaming, roasting, or lightly sautéing are better options.
- Variety is Key: Include a diverse range of vitamin E-rich foods in your diet throughout the week to ensure you’re getting a good balance of this essential nutrient.
Additional Considerations
- Fortified Foods: While not as prevalent as other vitamins, some breakfast cereals and spreads might be fortified with vitamin E. Check the label to see if these contribute to your daily intake.
Zinc
Regulating Oil Production and Reducing Inflammation
For those struggling with acne, zinc can be a valuable ally. This mineral helps regulate sebum production, the oil naturally produced by the skin. Excessive sebum can clog pores and create an environment conducive to acne breakouts. Zinc helps keep oil production in check, contributing to clearer skin. Furthermore, zinc possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe and reduce redness associated with acne lesions.
Zinc clears the skin by regulating oil production and combating inflammation. Here’s a closer look at how this essential mineral benefits your complexion:
- Oil Control: Zinc helps regulate sebum production, the oil naturally secreted by the skin. Excessive sebum can clog pores, creating an environment conducive to acne breakouts. Zinc acts as a natural sebum regulator, keeping oil production in check and preventing clogged pores. This can significantly reduce the occurrence of acne breakouts, particularly for those prone to oily skin.
- Anti-Inflammatory Powerhouse: Acne is an inflammatory skin condition. Zinc possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe and reduce redness associated with acne lesions. By mitigating inflammation, zinc can minimize the severity of breakouts and promote faster healing. Research suggests that zinc’s anti-inflammatory properties may help with other inflammatory skin conditions such as rosacea and eczema.
- Wound Healing: Zinc plays a vital role in wound healing by supporting tissue repair. This can benefit acne breakouts, as it can help wounds heal faster and potentially minimize scarring. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that oral zinc supplementation might help improve the appearance of acne scars. Zinc’s role in wound healing may also benefit other skin conditions involving tissue damage, such as minor cuts, scrapes, and insect bites.
- Potential Hormonal Balance: Zinc may offer additional benefits for some individuals, particularly women experiencing hormonal acne. Androgens are hormones that play a role in sebum production and can fluctuate during the menstrual cycle. Zinc may help regulate these hormonal fluctuations, potentially reducing sebum production and the occurrence of hormonal acne breakouts.
Dietary Sources: While supplements might be helpful in some cases, incorporating zinc-rich foods into your diet is a good way to ensure you’re getting enough of this essential mineral for overall health, including skin health.
Dosage and Form: The recommended daily intake (RDI) of zinc will be different depending on age and gender. It’s crucial to consult with a doctor before taking zinc supplements to determine the appropriate dosage for your needs. Excessive zinc intake can have adverse effects. Topical zinc can also be beneficial in some cases. However, consult a dermatologist to determine the best approach for your skin type and specific concerns.
Food Sources of Zinc

- Seafood: Oysters are rich in zinc, containing over 70 milligrams per serving, making them stand out. Other shellfish like crabs and lobster are also good sources. Fish like salmon and sardines are good options as well.
- Red Meat: Lean beef and lamb are good options, providing 5-7 milligrams of zinc per 3-ounce cooked serving.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey offer a source of dietary zinc, with an average of 2-3 milligrams per 3-ounce cooked serving.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent plant-based sources of zinc. A cup of cooked lentils provides approximately 5 milligrams of zinc, while chickpeas and beans offer around 3 milligrams per cup.
- Nuts and Seeds: Pumpkin seeds, cashews, and sesame seeds contribute to your daily zinc intake. Pumpkin seeds are rich in zinc, with a single ounce containing around 5 milligrams. Cashews and sesame seeds offer around 2 milligrams per ounce.
- Eggs: A versatile ingredient, eggs contain sufficient zinc. One whole egg contains around 5 milligrams of zinc.
B Vitamins (B3, B5)
The B vitamin complex plays a vital role in overall health, and several B vitamins, particularly B3 (niacinamide) and B5 (pantothenic acid), offer specific benefits for promoting clear skin. Here’s a breakdown of how these B vitamins can contribute to a radiant complexion:
Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide)
- Skin Barrier Hero: Niacinamide helps strengthen the skin’s natural barrier. This outermost layer protects against environmental aggressors like pollution and bacteria. A strong barrier is key for maintaining healthy, hydrated skin. Niacinamide can help prevent moisture loss and irritation by improving barrier function, leading to a smoother, healthier appearance.
- Oil Control and Pore Minimization: Niacinamide, like zinc, can regulate sebum production. Excess sebum can clog pores and contribute to acne breakouts. By keeping oil production in check, niacinamide can help prevent clogged pores, minimize their appearance, and reduce the risk of breakouts.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Niacinamide contains anti-inflammatory properties that can soothe and reduce redness associated with acne lesions. Like zinc, it can minimize the severity of breakouts and promote faster healing.
- Hyperpigmentation Fighter: Niacinamide can help reduce hyperpigmentation, which is the darkening of certain areas of skin. It does this by inhibiting the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Niacinamide can help lighten dark spots by lowering melanin production and promoting even skin tone. This can be beneficial for those struggling with sun damage, acne scars, and hyperpigmentation.
How to Get Vitamin B3 (Niacinamide)?
- Dietary Sources: Foods like chicken, fish, eggs, and legumes contain some vitamin B3. However, topical application is generally considered more effective for improving skin health.
- Topical Products: Niacinamide is a popular ingredient in many skincare products, such as serums, moisturizers, and creams. For optimal benefits, look for products with a concentration of 3-5%.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Hydration Hero: Vitamin B5 acts as a humectant, a substance that attracts and retains moisture in the skin. This helps keep skin hydrated and plump, contributing to a healthy, youthful appearance. Dehydrated skin can appear dull and rough, worsening the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. By promoting hydration, vitamin B5 can help improve skin texture and elasticity.
- Soothing and Calming: Vitamin B5 can help soothe and calm irritated skin. This can benefit those with conditions like eczema or psoriasis, which can cause redness, dryness, and discomfort.
- Wound Healing: Like other B vitamins, vitamin B5 plays a role in wound healing by supporting tissue repair. This can benefit acne breakouts or other skin conditions involving tissue damage, potentially minimizing scarring.
How to Get Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)?
- Dietary Sources: Many foods are good sources of vitamin B5, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, avocados, yogurt, whole grains, and legumes.
- Topical Products: Some skincare products, such as moisturizers and creams, may contain vitamin B5.
Combining B Vitamins for Synergistic Effects
B vitamins often work synergistically, meaning they work together to achieve a greater effect than individually. Including B3 (niacinamide) and B5 (pantothenic acid) in your skincare routine can offer a well-rounded approach to promoting clear skin. Niacinamide can address oil control, inflammation, and hyperpigmentation, while vitamin B5 can enhance hydration and soothe irritation. Together, they can create a powerful duo for achieving clearer, healthier skin.
Additional Considerations
- Diet and Supplements: While a balanced diet rich in B vitamins is essential for overall health, topical application of niacinamide is generally considered more effective for improving skin health. Consult a doctor before taking B vitamin supplements, as excessive intake can have side effects.
- Choosing the Right Products: When looking for skincare products containing B vitamins, check the ingredient list and look for niacinamide and panthenol (the active form of vitamin B5).
Food sources for Vitamin B3 (Niacin) and Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
While topical application of niacinamide is generally considered more effective for improving skin health, incorporating these dietary sources can contribute to your overall B3 intake:

- Meat, Poultry, and Fish: Excellent sources include chicken, turkey, salmon, tuna, and beef liver. The liver is particularly rich in B3, but be careful of portion due to its high vitamin A content.
- Eggs: A good source of B vitamins, including niacin.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas offer a plant-based source of B3.
- Nuts and Seeds: Peanuts, peanut butter, sunflower seeds, and peanuts are good options.
- Fortified Foods: Some breakfast cereals and grain products may be fortified with niacin. Check the label for confirmation.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
The beauty of vitamin B5 is that it’s widely found in many foods, making it easier to incorporate into your diet:

- Meat, Poultry, and Fish: Similar to B3, sources like chicken, turkey, fish, and beef (including organ meats like liver) are good providers of B5.
- Eggs: Another excellent source of B vitamins, including pantothenic acid.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese contribute to your daily B5 intake.
- Avocados: This creamy fruit is not only delicious but also a good source of vitamin B5.
- Whole Grains: Whole-wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and other whole grains are packed with B vitamins, including B5.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas offer a plant-based source of B5.
- Vegetables: While not the most concentrated sources, vegetables like broccoli, sweet potatoes, and mushrooms also contribute some vitamin B5.
Tips for Maximizing B Vitamin Absorption
- Variety is Key: Throughout the week, include a diverse range of B vitamin-rich foods from all the categories mentioned above in your diet. This ensures you get a good balance of all B vitamins, including B3 and B5.
- Balance with Healthy Fats: Some B vitamins, like B3, are fat-soluble. Including healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, or nuts in your meals can aid in absorbing B vitamins.
- Cooking Methods: While some cooking is necessary, minimize harsh methods like frying to preserve B vitamin content. Steaming, roasting, or lightly sautéing are better options.
Beyond Vitamins: A Holistic Approach for Clear Skin
While these vitamins offer significant benefits, it’s important to remember that they are not a magic bullet for clear skin. A holistic approach that combines them with a healthy lifestyle yields the best results. Here are some additional tips:
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains gives your body the essential nutrients for healthy skin function. It also ensures you’re getting a good balance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that improves skin health.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps keep skin hydrated and plump. Aim for eight glasses of water daily. Dehydrated skin can appear dull and rough, worsening the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
- Sleep: Proper sleep allows your body to repair and regenerate cells, including skin cells. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night for optimal skin health.
- Skincare Routine: A skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and sun protection is crucial. Choose products that suits your skin type and use sunscreen daily, even on cloudy days.
- Stress Management: Stress can have adverse effects on your skin. Try to manage stress by practicing activities such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Consulting a Dermatologist
If you are experiencing persistent skin issues, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist. A dermatologist can evaluate your specific needs and suggest a customized treatment plan consisting of a blend of dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, topical medications, and, if necessary, vitamin supplements. It is crucial to consult a doctor before taking any supplements to guarantee a safe and appropriate dosage.
Conclusion
Vitamins A, C, E, B3 & B5, and Zinc are powerful allies for clear skin. Incorporating these nutrients into your diet alongside a healthy lifestyle can promote skin health and achieve that coveted radiant glow. Remember, consistency is key! Aim for a balanced diet, prioritize sleep, manage stress, and maintain a consistent skincare routine. With dedication and the right combination of strategies, you can unlock the power of your body’s natural tools for clear, healthy skin.
